II. Graphs and Charts on Rehabilitation Services for People with Mental
Retardation
A. Health and Medical Care
Infant mortality in Japan is now one of the lowest in the world. The improvement of
maternal and child health has brought changes in the disease structure, so that mental
retardation and congenital malformation have now become prominent among the causes of
disabilities in children. Health and medical care programs for persons with mental
retardation are classified into prevention, early detection and intervention, and
multidisciplinary care for persons with severe disabilities.
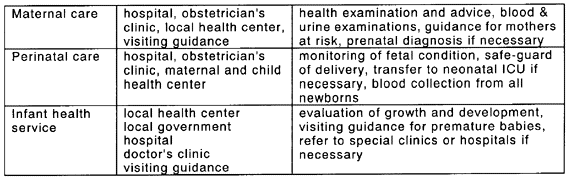
1. Prevention and Early Intervention Services in Japan
Prevention of mental retardation is one of the most important objectives of maternal
and child health services. Health examination and guidance for pregnant women,
monitoring of the condition of the fetus, and safe delivery in the hospital have been
encouraged. These policies have resulted in decreasing numbers of low-weight babies and
decreasing perinatal mortality, as well as fewer children with cerebral palsy.
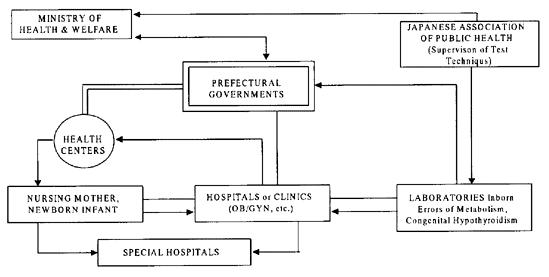
2. Mass Screening Program for Inborn Errors of Metabolism and Congenital
Hypothyroidism
From 1977, a nationwide newborn mass screening program has been conducted to detect inborn
errors of metabolism. During 1990 and 1991, 99.8% of all live birth in Japan were subjected
to blood collection for the Guthrie test this screening program has almost eliminated the
occurrence of mental retardation associated with phenylketonuria and cretinism. The success
of this program was facilitated by the fact that 99.8% of birth are now delivered in hospitals,
obstetricians' clinics, and maternal and child health centers.
前ページ 目次へ 次ページ